Job Scheduling with HTCondor
Objectives
- Learn how to submit HTCondor jobs.
- Learn how to monitor the running jobs.
Overview
In this section, we will learn the basics of HTCondor in submitting and monitoring workloads, or "jobs". The jobs are submitted through the submit host. The submitted jobs are executed on the remote worker node(s) and the outputs are transfered back to the login node. In the HTCondor job submit file, we have to describe how to execute the program and transfer the output data.
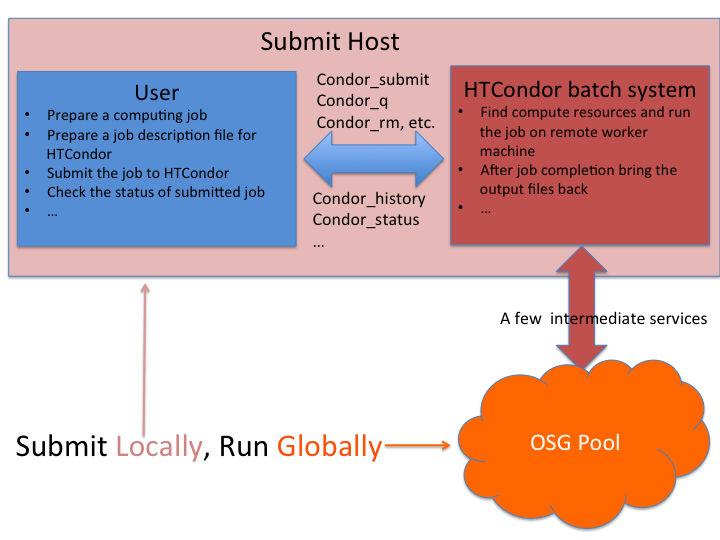
Login to Submit Host
First, we log in to the submit host:
ssh username@training.osgconnect.net # username is your username
password: # enter your password
We will get our example files using tutorial.
Let's get started with the quickstart tutorial:
$ tutorial quickstart # creates a directory "tutorial-quickstart"
$ cd tutorial-quickstart # script and input files are inside this directory
We will look at two files in detail: short.sh and tutorial01.submit
Job execution script
Inside the tutorial directory, open up short.sh in an editor.
$ nano short.sh
This is a shell script, quite ordinary.
#!/bin/bash
# short.sh: a short discovery job
printf "Start time: "; /bin/date
printf "Job is running on node: "; /bin/hostname
printf "Job running as user: "; /usr/bin/id
printf "Job is running in directory: "; /bin/pwd
echo
echo "Working hard..."
sleep 20
echo "Science complete!"
To close nano, hold down Ctrl and press X. Press Y to save, and then
Enter Now, make the script executable. Recall that this is not
necessary for shell programs that you create and run locally. However,
it is extremely important for jobs running on the grid. So is the
"shbang" line (#!/bin/bash).
$ chmod +x short.sh
Since we used the tutorial command, all files are already in your workspace. Run the job locally when setting up a new job type – it is good to test your job outside of HTCondor before submitting into the Open Science Grid.
$ ./short.sh
Start time: Mon Mar 6 00:08:06 CST 2017
Job is running on node: training.osgconnect.net
Job running as user: uid=46628(username) gid=46628(username) groups=46628(username),400(condor),401(ciconnect-staff),1000(users)
Job is running in directory: /tmp/Test/tutorial-quickstart
Working hard...
Science complete!
Job description file
So far, so good! Next we will create a simple (if verbose) HTCondor submit file. A submit file tells the grid software how to run your workload, with what properties and arguments, and how to collect and return output to you.
$ nano tutorial01.submit
# The UNIVERSE defines an execution environment. You will almost always use VANILLA.
Universe = vanilla
# EXECUTABLE is the program your job will run It's often useful
# to create a shell script to "wrap" your actual work.
Executable = short.sh
# ERROR and OUTPUT are the error and output channels from your job
# that HTCondor returns from the remote host.
Error = job.error
Output = job.output
# The LOG file is where HTCondor places information about your
# job's status, success, and resource consumption.
Log = job.log
# QUEUE is the "start button" - it launches any jobs that have been
# specified thus far.
Queue 1
Job submission
Submit the job using condor_submit.
$ condor_submit tutorial01.submit
Submitting job(s).
1 job(s) submitted to cluster 1144.
Job status
Your first job is on the grid! The condor_q command tells the status of
currently running jobs. Generally you will want to limit it to your own
jobs by adding your own username to the command.
$ condor_q username
-- Schedd: training.osgconnect.net : <192.170.227.119:9419?...
ID OWNER SUBMITTED RUN_TIME ST PRI SIZE CMD
1144.0 username 3/6 00:17 0+00:00:00 I 0 0.0 short.sh
1 jobs; 0 completed, 0 removed, 1 idle, 0 running, 0 held, 0 suspended
If you want to see all jobs running on the system, use condor_q without
any extra parameters. You can also get status on a specific job
cluster – the number that condor_submit gave you.
$ condor_q 1144.0
-- Schedd: training.osgconnect.net : <192.170.227.119:9419?...
ID OWNER SUBMITTED RUN_TIME ST PRI SIZE CMD
1144.0 username 3/6 00:17 0+00:00:07 R 0 0.0 short.sh
1 jobs; 0 completed, 0 removed, 0 idle, 1 running, 0 held, 0 suspended
A job cluster identifies one batch of jobs. The batch could have one job or ten thousand in it – what matters is that each time a submit file says "Queue", you get a cluster. The individual jobs within a job cluster are identified by the numbers after the dot in the job ID – so in this example, 1144 is the job cluster, and 1144.0 is the job ID (or jobid) of job 0 in that cluster.
Note the ST (state) column. Your job will be in the I state (idle) if it hasn't started yet. If it's currently scheduled and running, it will have state R (running). If it has completed already, it will not appear in condor_q.
You may sometimes see jobs in H state. These are held jobs. Held jobs are stalled, usually for a specific reason, and won't progress until released. Until you gain savvy with diagnosing why a job is held and solving it on your own, you may contact the OSG support team for help with held jobs.
Let's wait for your job to finish – that is, for condor_q not to show the job in its output.
$ condor_q username | tail -1
1 jobs; 0 completed, 0 removed, 0 idle, 1 running, 0 held, 0 suspended
You could run this over and over to watch for the job to complete – but
watch can make this simpler. Let's submit the job again, and
watch condor_q output at five-second intervals. Your first
job has probably already completed by now, so submit a new one first:
$ condor_submit tutorial01.submit
Submitting job(s).
1 job(s) submitted to cluster 1145
$ watch -n 5 "condor_q $USER 2>/dev/null"
When your job has completed, it will disappear from the list. To close
watch, press control-C – hold down Control and press C.
Job history
Once your job has finished, you can get information about its execution
from the condor_history command:
$ condor_history 1144
ID OWNER SUBMITTED RUN_TIME ST COMPLETED CMD
1144.0 osguser50 3/6 00:17 0+00:00:27 C 3/6 00:28 /share/training/..
You can see much more information about your job's final status using the -long option.
Job output
Once your job has finished, you can look at the files that HTCondor has returned to the working directory. If everything was successful, it should have returned:
- a log file from Condor for the job cluster:
job.log - an output file for each job's output:
job.output - an error file for each job's errors:
job.error
Read the output file. It should be something like this:
$ cat job.output
Start time: Wed Mar 8 18:16:04 CST 2017
Job is running on node: cmswn2300.fnal.gov
Job running as user: uid=12740(osg) gid=9652(osg) groups=9652(osg)
Job is running in directory: /storage/local/data1/condor/execute/dir_2031614/glide_6B4s2O/execute/dir_887949
Working hard...
Science complete!
Unscheduling jobs
Once you know how to create files, you want to know how to delete
them. And once you can schedule workloads across thousands of computers
simultaneously, you need to know how to remove them. The command for that
is condor_rm, and it takes only one argument: the job cluster or job ID.
$ condor_submit tutorial01.submit
Submitting job(s).
1 job(s) submitted to cluster 1145
$ condor_rm 1145
Cluster 1145 has been marked for removal.
Sometimes it is useful to remove all your jobs. You can do that by specifying your username as argument for condor_rm:
$ condor_submit tutorial01.submit
Submitting job(s).
1 job(s) submitted to cluster 1146
$ condor_rm username
All jobs of user "username" have been marked for removal
Basics of HTCondor Matchmaking
As you have seen in the previous lesson, HTCondor is a batch management system that handles running jobs on a cluster. Like other full-featured batch systems, HTCondor provides a job queueing mechanism, scheduling policy, priority scheme, resource monitoring, and resource management. Users submit their jobs to HTCondor scheduler. HTCondor places them into a queue, chooses when and where to run the jobs based upon a policy, carefully monitors their progress, and ultimately informs the user upon completion. This lesson will go over the some of the specifics of how HTCondor selects compute nodes where it should run particular jobs.
HTCondor selects nodes on which to run particular jobs using a matchmaking process. When a job is submitted to HTCondor, HTCondor generates a set of attributes that the job needs in order to run. These attributes function like classified ads in the newspaper and are called classads. The classads for a job indicate what it is looking for, just like a help wanted ad. For example:
Requirements = OSGVO_OS_STRING == "RHEL 6" && Arch == "X86_64" && HAS_MODULES == True
Let's examine what a machine classad looks like. This is a two step process, first we get a name for one of the machines, and then we ask condor_status to give us the details for that machine (-long).
$ condor_status -pool osg-flock.grid.iu.edu -af Name | head -n 1
[resource name]
$ condor_status -long -pool osg-flock.grid.iu.edu [resource name] | sort
HAS_FILE_usr_lib64_libgfortran_so_3 = true
HAS_MODULES = false
OSGVO_OS_STRING = "RHEL 6"
HTCondor takes a list of classads from jobs and from compute nodes and then tries to make the classads with job requirements with the classads with compute node capabilities. When the two match, HTCondor will run the job on the compute node.
A Basic OSG Job
You can make use any of these attributes to limit where your jobs go. The following
is a fairly complete OSG job which you can use when getting started on OSG. Note
the Requirements and requests_* lines.
# The UNIVERSE defines an execution environment. You will almost always use VANILLA.
Universe = vanilla
# These are good base requirements for your jobs on OSG. It is specific on OS and
# OS version, core cound and memory, and wants to use the software modules.
Requirements = OSGVO_OS_STRING == "RHEL 6" && Arch == "X86_64" && HAS_MODULES == True
request_cpus = 1
request_memory = 1 GB
# EXECUTABLE is the program your job will run It's often useful
# to create a shell script to "wrap" your actual work.
Executable = short.sh
# ERROR and OUTPUT are the error and output channels from your job
# that HTCondor returns from the remote host.
Error = job.$(Cluster).$(Process).error
Output = job.$(Cluster).$(Process).output
# The LOG file is where HTCondor places information about your
# job's status, success, and resource consumption.
Log = job.log
# Send the job to Held state on failure.
on_exit_hold = (ExitBySignal == True) || (ExitCode != 0)
# Periodically retry the jobs every 60 seconds, up to a maximum of 5 retries.
periodic_release = (NumJobStarts < 5) && ((CurrentTime - EnteredCurrentStatus) > 60)
# QUEUE is the "start button" - it launches any jobs that have been
# specified thus far.
Queue 1
You can test this job by submitting and monitoring it as we have just covered:
$ condor_submit osg-template-job.submit
Submitting job(s).
1 job(s) submitted to cluster 1151
The filenames for this job includes a job id, which means that if you submit more than one job, they will all have unique outputs.
$ ls *.output
job.1151.0.output
job.1152.0.output
Key Points
- HTCondor shedules and monitors your Jobs.
- To submit a job to HTCondor, you must prepare the job execution and job submission scripts.
- condor_submit - HTCondor's job submission command.
- condor_q - HTCondor's job monitoring command.
- condor_rm - HTCondor's job removal command.
Challenges
What happens if we leave the Queue line out of a submit file?
What happens if we write only Queue, with no argument?
condor_history -long username gives a LOT of extended information about
your past jobs, ordered as key-value pairs. Try it with your a single
job from your last cluster:
$ condor_history -long ######.0
Included among these attributes is the RemoteWallClockTime parameter,
which tells how long your job ran on the remote worker. How might you
collect this value across all your historical jobs?
(Remember that the grep command can be used to pick out specific
patterns from text.)
